Reed Sensor – Magnetic Proximity Switches
High-reliability magnetic proximity sensors for industrial automation, security systems, and IoT applications. Custom configurations available for OEM projects.

What is a Reed Sensor?
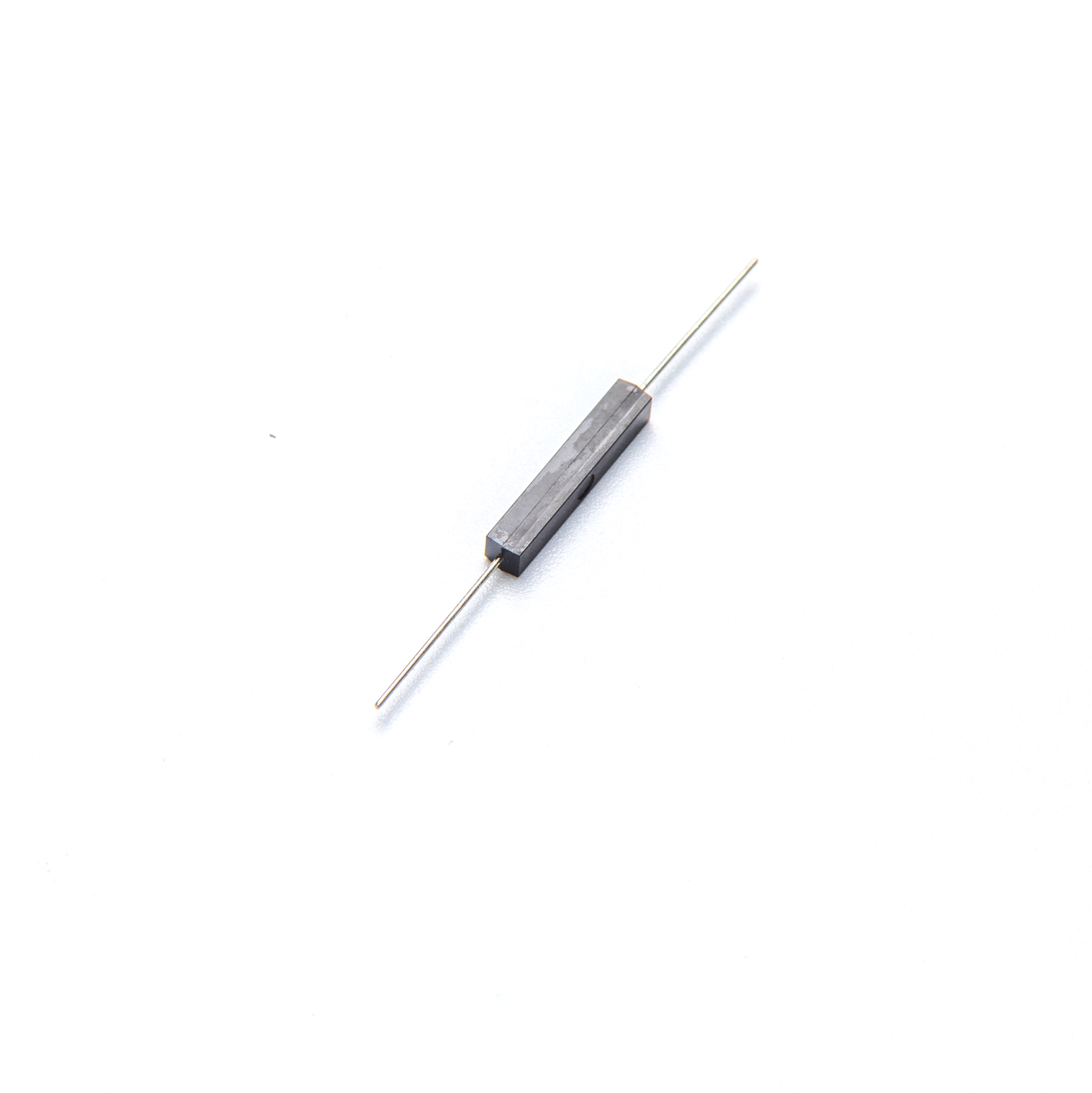
A reed sensor is a magnetic proximity switch that activates when a magnetic field is present. It consists of two ferromagnetic reed blades sealed in a glass capsule, making it ideal for harsh environments and long-life applications.
Key Advantages:
- Up to 10^9 operations – extremely long service life
- Hermetically sealed – works in dust, humidity, and liquids
- No power required for sensing – zero standby current
- Compact size – fits in tight spaces
- EMI resistant – no false triggering
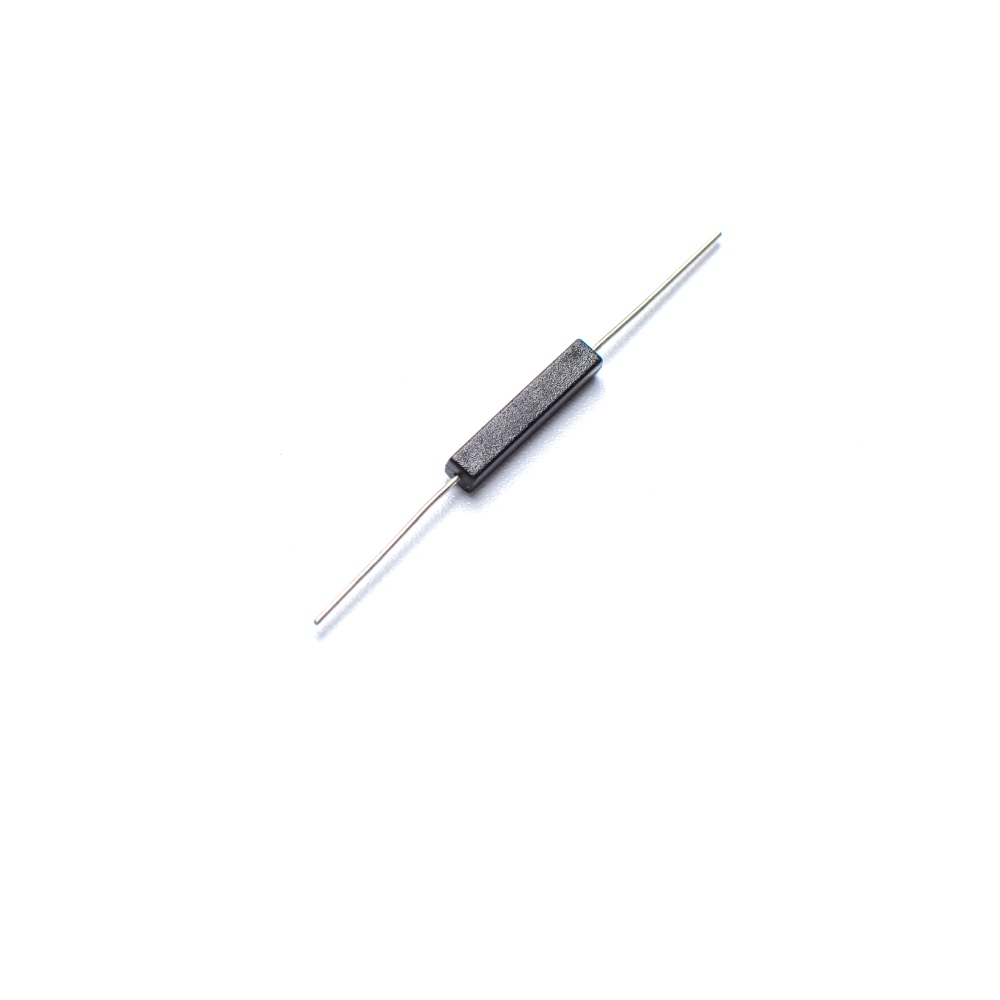

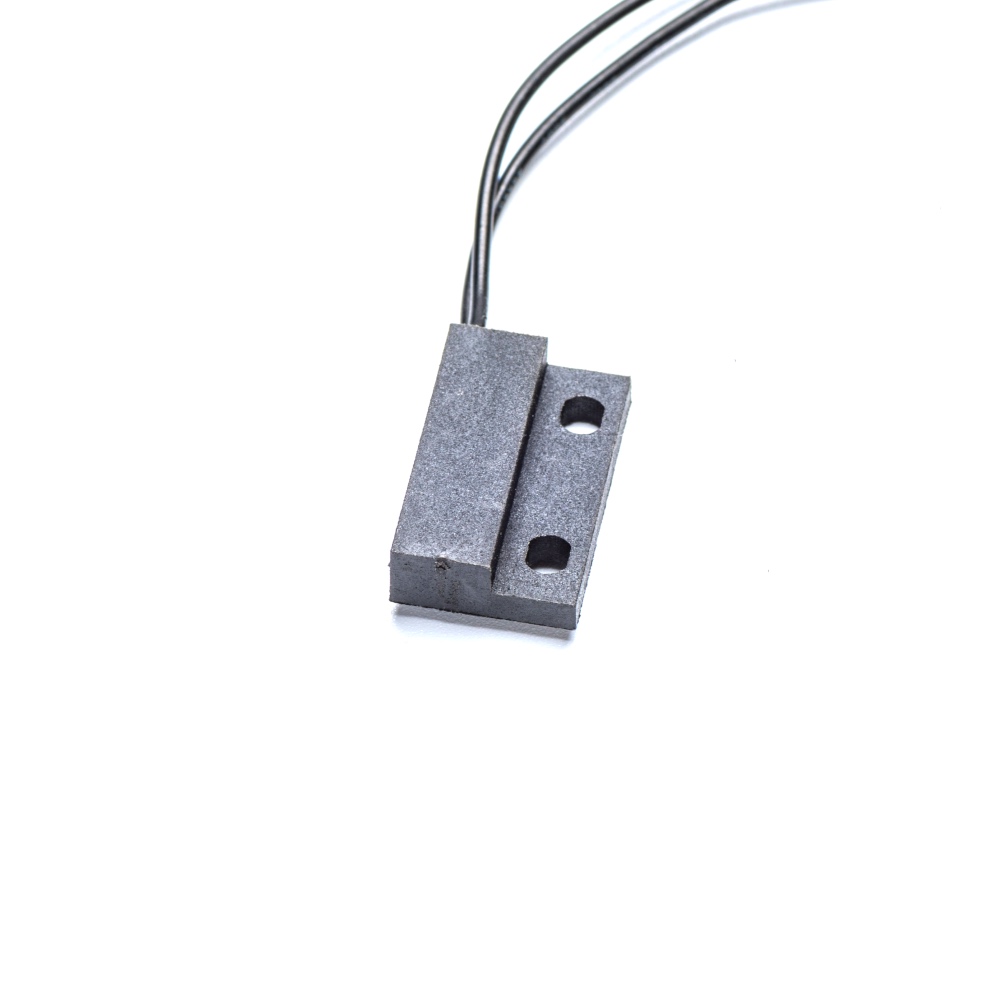
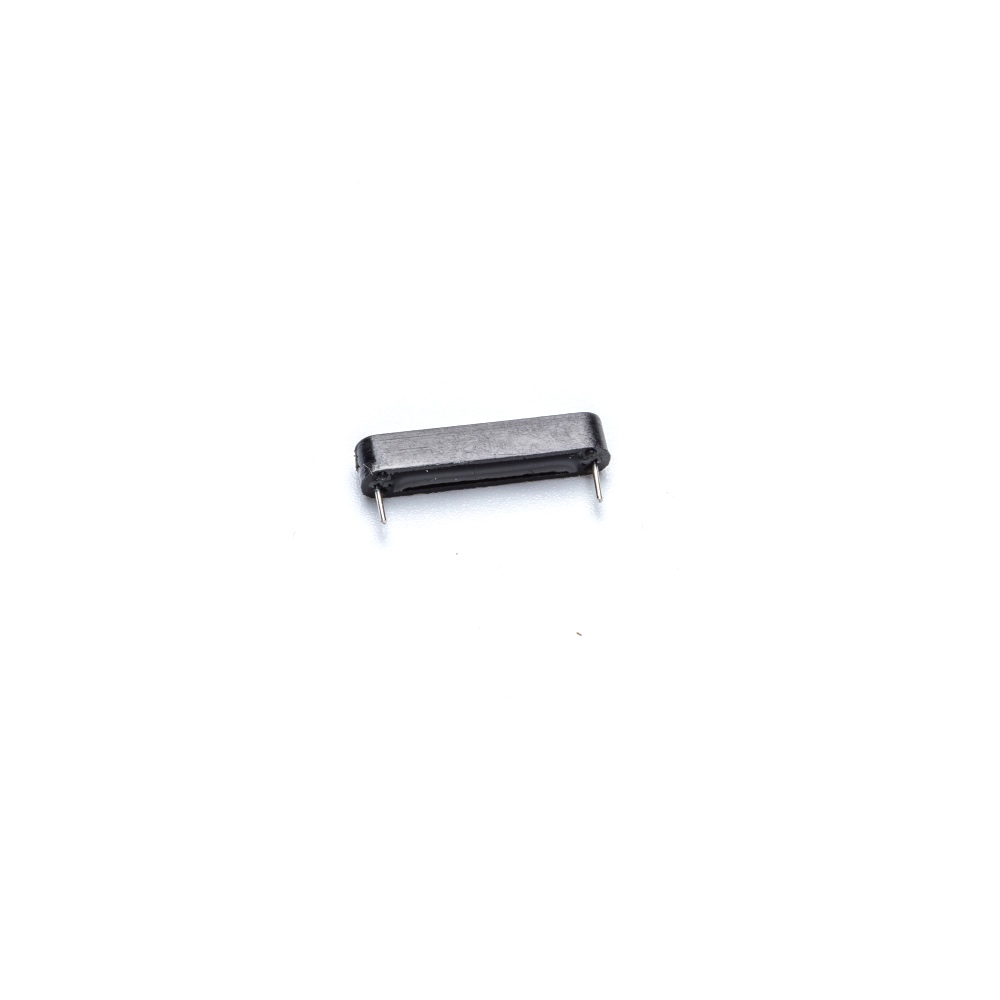
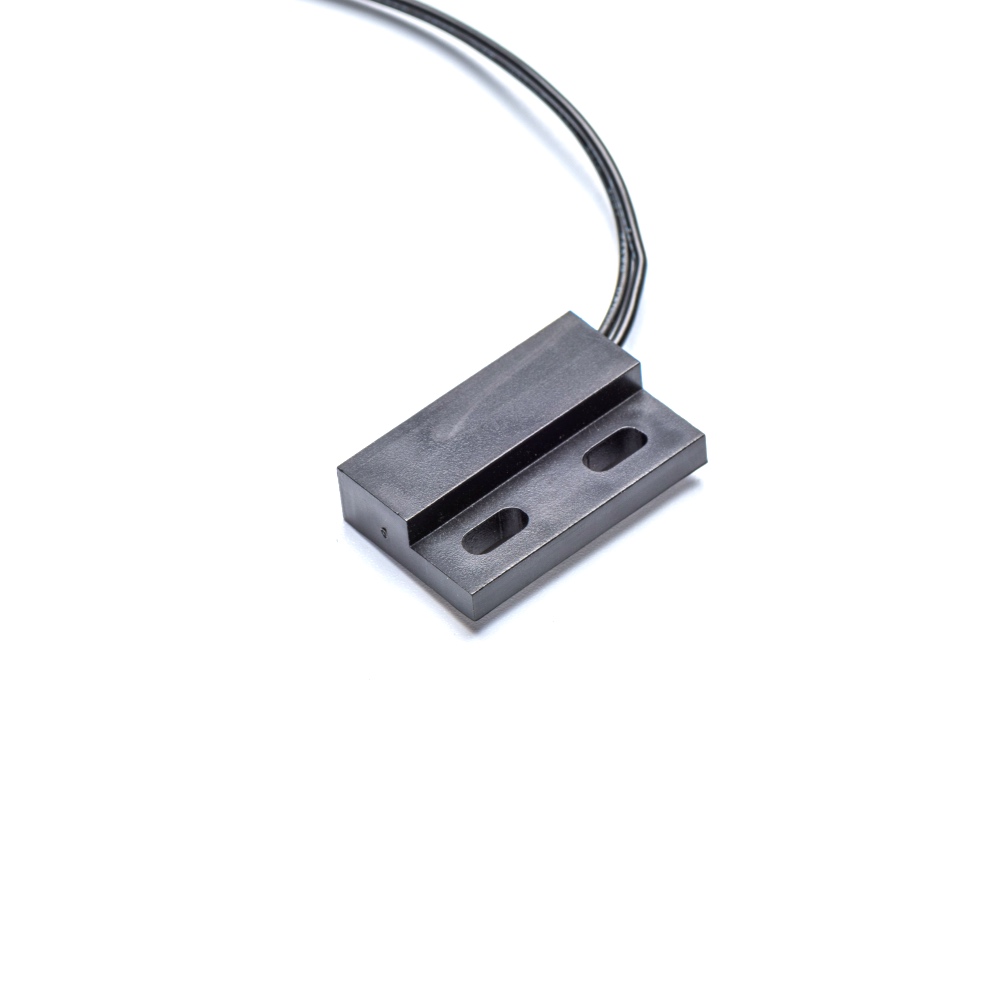
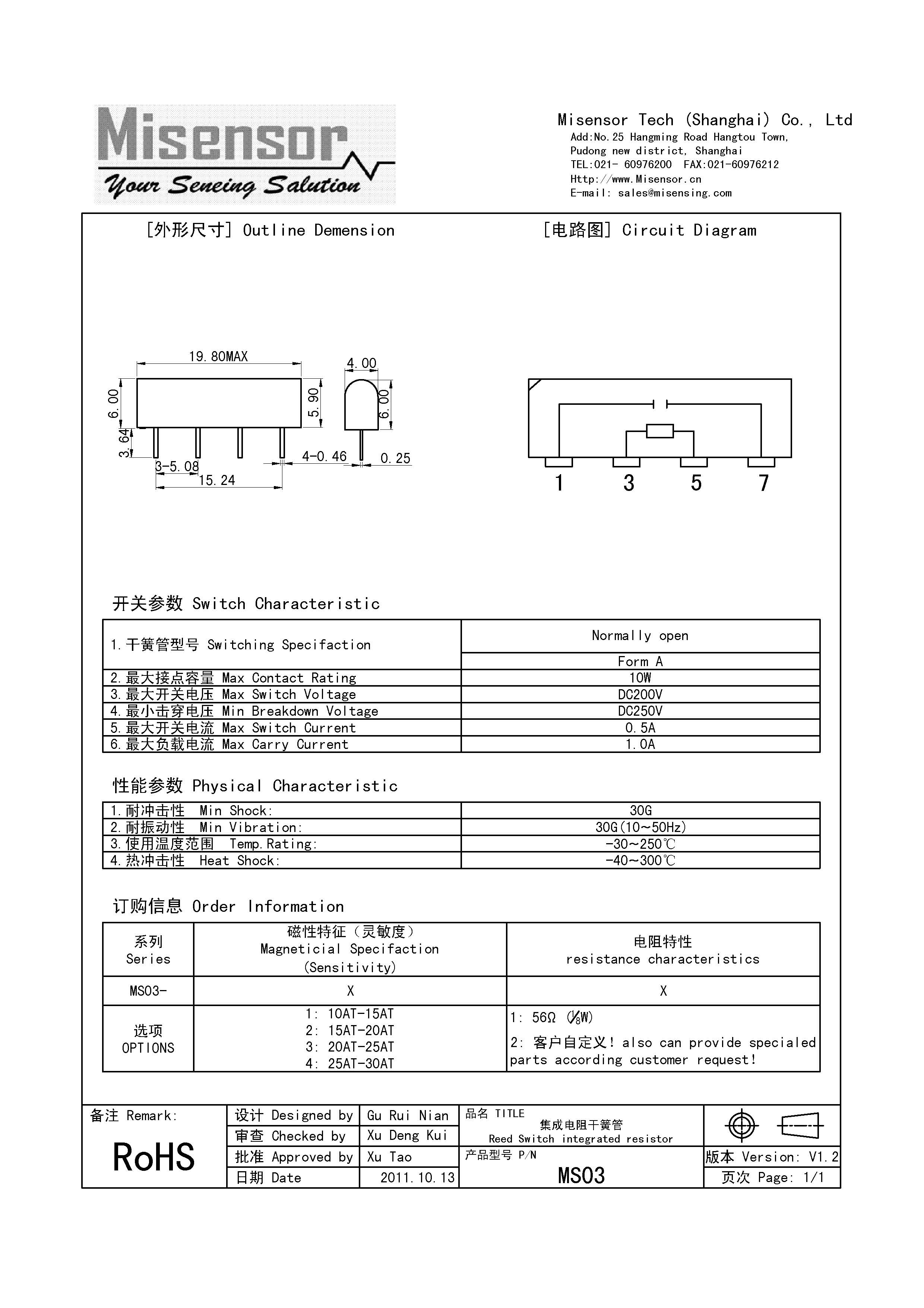
Product Models
Industrial Applications
Security Systems
Door/window sensors, alarm triggers
Industrial Automation
Position sensing, limit switches
Automotive
Door locks, seat belts, trunk sensors
Smart Home
IoT devices, appliance control
Medical Equipment
Equipment covers, safety interlocks
RoHS Compliant
REACH Ready
UL Listed Options
Need Custom Reed Sensor Solutions?
Our engineering team provides custom sensor configurations for OEM applications. Share your requirements for a tailored solution.