Low Power Switching for Battery Instruments
Maximizing battery life with Hermetic Reed Relay technology.
The Challenge of Remote Power
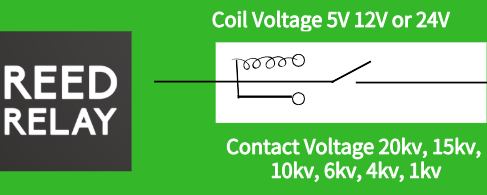
 Reed Relays in Portable Instrumentation
Reed Relays in Portable Instrumentation
Nowadays, more and more instruments are used in places far away from conventional power sources, such as remote environmental monitoring stations, handheld field meters, and portable medical diagnostic tools. These devices can only rely on battery power.
Therefore, any electronic component used in the design must have very low power consumption requirements to enable longer working times and reduce the frequency of battery replacement or charging.
Why Reed Relays?
The reed relay is an outstanding switching device for these applications. Its contacts are sealed in a glass envelope, providing good airtightness and protection against environmental factors such as dust and moisture.
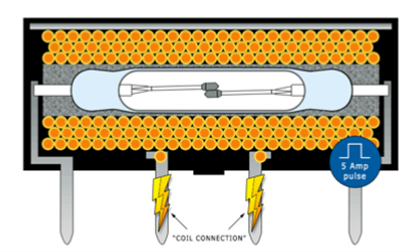 Operating Principle: Magnetic Flux Actuation
Operating Principle: Magnetic Flux Actuation
 Hermetically Sealed Glass Structure
Hermetically Sealed Glass Structure
This construction provides key advantages for battery-powered circuits:
- Isolation: Superior insulation performance between contacts and coil prevents leakage currents.
- Low Resistance: Very low and stable contact resistance provides assurance for wide bandgap load circuits.
- Zero Leakage: Unlike semiconductors, open contacts consume absolutely zero power.
The Bistable (Latching) Advantage
For maximum efficiency, we recommend Latching (Bistable) Reed Relays. These relays use a permanent magnet to hold the contacts in the closed state without any continuous coil power. Power is only consumed for a few milliseconds during the switching pulse, resulting in effectively Zero Power Consumption while the relay is static.
Recommended Product Solutions
MSIP Series
Miniature Single-In-Line. Available in high-resistance coil options to minimize current draw.
View Datasheet →